Breaking Barriers: Successful Iliac CTO Procedure Reopens 100% Blocked Artery Without Surgery
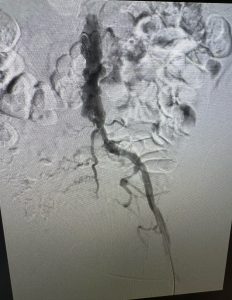
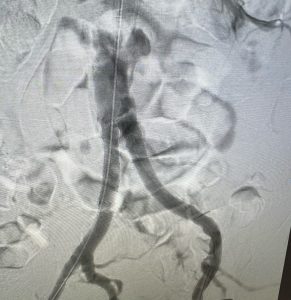
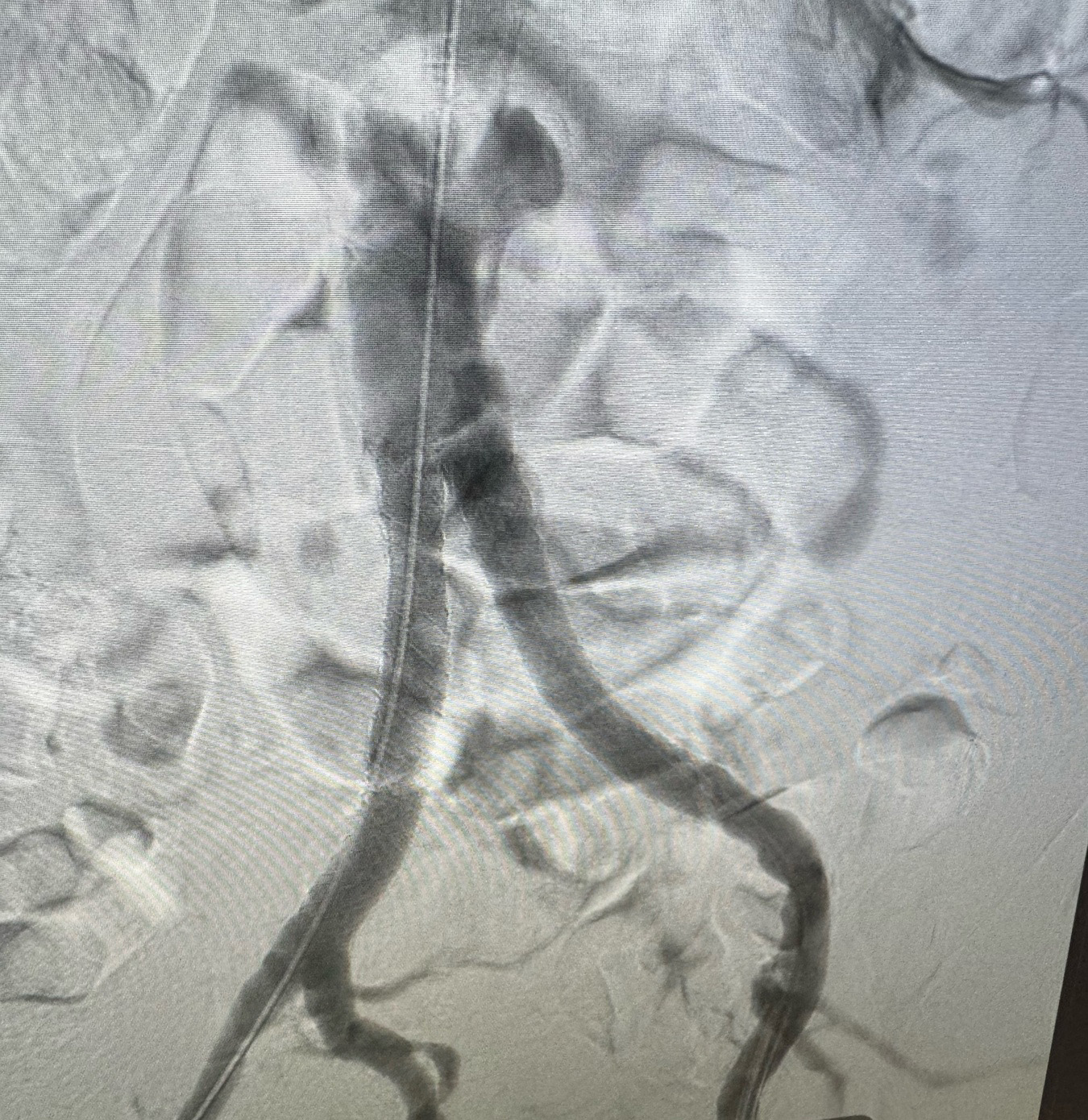
Dr. Micaela Iantorno recently collaborated with Dr. Sadie Ahanchi to treat a patient with a completely blocked iliac artery, which was significantly impacting his quality of life and was posing a potential life-threatening risk if left untreated. The patient had previously undergone an unsuccessful endovascular procedure, so the surgical team considered bypass surgery as the next option. After thorough discussions, they decided to pursue an alternative endovascular approach using a reentry technique. Using advanced imaging and catheter technology, they successfully opened the obstruction and restored blood flow.
The accompanying images illustrate the total occlusion in the patient’s arteries before the procedure, as well as a subsequent image showing restored blood flow. The results were remarkable, as the patient experienced immediate relief and improved mobility. This case underscores the importance of multidisciplinary teamwork and innovative techniques in managing complex vascular issues, demonstrating how timely intervention can lead to positive outcomes for patients.
The Critical Role of Oxygenated Blood Flow
Iliac arteries play a crucial role in delivering oxygenated blood to the lower parts of the body. If left untreated, severe complications can ensue such as:
1. Limb ischemia: This is a medical condition where there is inadequate blood flow. Patients experience pain, numbness, weakness, dysfunction and non-healing sores in the affected limb.
2. Tissue damage: Without adequate blood supply, the tissues in the affected area start to deteriorate and can eventually die (necrosis). Patients will begin to see ulcers and sores on the skin, which are slow to heal.
3. Gangrene: If blood flow isn’t restored, tissue may become gangrenous, necessitating surgical removal or even amputation.
4. Infection: Impaired blood flow can compromise the immune response in the affected area, making it easier for infections to occur.
5. Systemic complications: The lack of blood flow can prompt systemic effects, including the risk of cardiovascular events and complications related to chronic ischemia in other parts of the body.
Many individuals may not exhibit obvious symptoms but often report decreased mobility, pain and a reduced quality of life over time. Timely medical intervention is crucial to prevent serious outcomes and improve the chances of restoring blood flow while preserving the limb.